The pretty parts that make electronics fast and uncomplicated to use also make their disposal an environmental nightmare. Parts of smartphones, desktops and even kitchen appliances have large metals and other compounds that are poisonous to us and destructive to ecosystems.
As electronics turn into less costly to purchase, e-waste has piled up. A 2019 report from the World Economic Discussion board identified as e-squander “the speediest-developing waste stream in the globe”—and for excellent explanation. That same yr, people generated a lot more than 50 million metric tons of e-waste, in accordance to the U.N.’s World-wide E-squander Monitor. A great deal of it is incinerated, piled up in landfills or exported to lessen-revenue nations around the world wherever it creates public overall health and environmental dangers.
A few researchers in the University of Washington Faculty of Engineering are checking out means to make electronics far more Earth-welcoming. Vikram Iyer, an assistant professor in the Paul G. Allen School of Laptop or computer Science & Engineering and researcher in the UW Institute for Nano-engineered Devices, will be presenting a useful computer mouse with a biodegradable situation and circuit board at the CHI 2022 convention in May. Aniruddh Vashisth, an assistant professor of mechanical engineering, is creating artificial resources that—unlike plastics—can be recycled and reused indefinitely. And Eleftheria Roumeli, an assistant professor of materials science and engineering and researcher in the Molecular Engineering & Sciences Institute, takes advantage of biological supplies, this kind of as seaweeds and other algae, to establish possibilities to plastics that can be 3D-printed.
For Earth Working day, UW News reached out to these engineers to go over their tasks.
What capabilities do you prioritize when creating sustainable electronics?
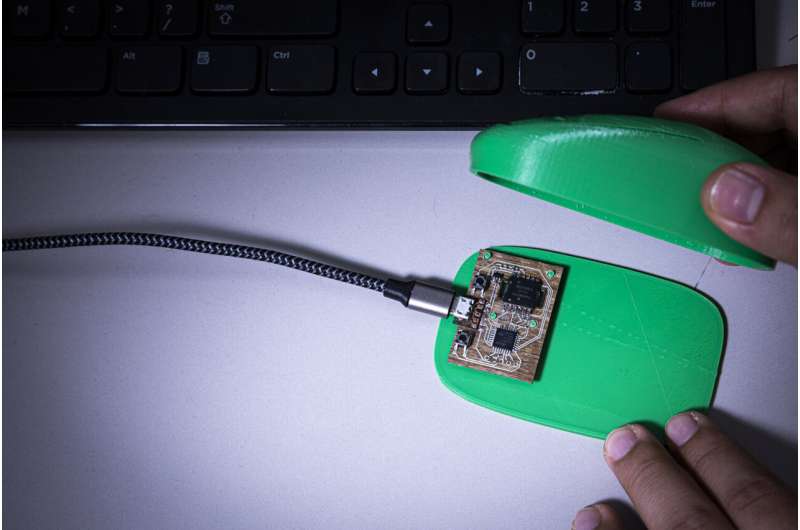
Vikram Iyer: There are heaps of vital complications to tackle in designing sustainable electronics, like lessening the environmental effect of e-squander. Our teams are striving to develop artistic answers to this difficulty, such as applying new and a lot more environmentally helpful components when making purposeful devices that you should not compromise general performance. For instance, the mouse we developed with a biodegradable circuit board operates when you plug it into any pc.
What was the style method like for the mouse?
VI: This task was a collaboration with Bichlien Nguyen, a principal researcher at Microsoft, and Vicente Arroyos, a UW doctoral scholar in the Allen University. We took quite a few methods to make this mouse:
- We optimized our circuit style to use the fewest quantity of silicon chips possible, simply because all around 80% of carbon emissions affiliated with producing electronics comes from the power-intensive procedures applied to make chips.
- We use biodegradable elements when attainable. For case in point, the circuit board that holds and connects the chips with each other normally incorporates poisonous flame-retardants, but we alternatively pattern our circuits on a board designed from flax fibers. Also, the casing for the mouse is produced out of biodegradable plastics.
- We use typical-function, programmable chips, like microcontrollers, in our styles so that we can reuse them in new products.
- We use software package to estimate the environmental influence of each individual stage of creation to quantify the environmental impacts and discover which phases of our structure to boost future.
This is just a start out, and our extended-phrase eyesight is to develop new elements and procedures that support us deliver a generation cycle for electronics in which all the products and elements can possibly be recycled and reused, or degraded and regenerated by means of the natural organic cycle.
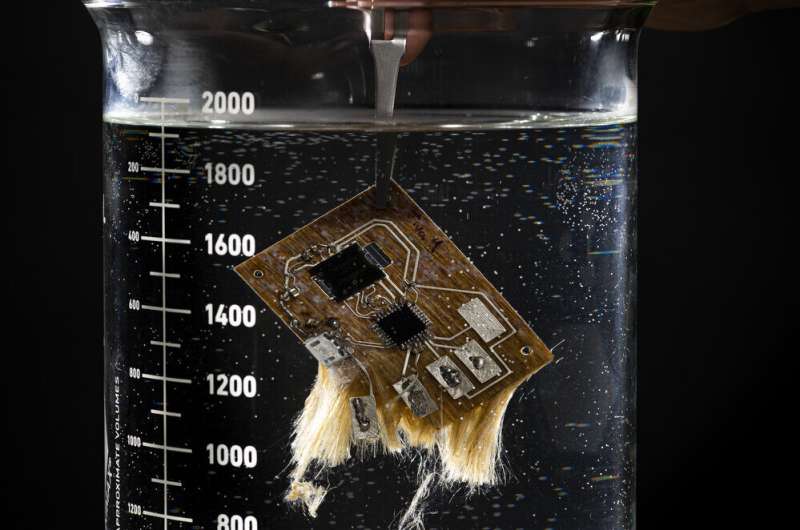
Is it really true that the mouse’s circumstance and circuit board dissolve in drinking water?
VI: When we submerge our circuit board in drinking water, the fibers get started to come aside and the complete factor just disintegrates. This requires about 5 to 10 minutes in hot water, or a couple several hours at area temperature. After this we are still left with the chips and circuit traces which we can filter out. We also created two distinct cases, one particular of these can dissolve in water and the other can be commercially composted.
Would a biodegradable mouse be as sturdy as a conventional mouse, specifically up from the physique heat and dampness we produce?
VI: There are certainly sustainable strategies to make certain biodegradable components are also tough. For case in point, you could add a skinny coating of drinking water-repellent supplies to the mouse—like chitosan, which is observed the natural way in the outer skeleton of shellfish. We also present that we can print the circumstance out of polylactic acid, a substance typically employed to make things like commercially compostable forks. Heading forward we’re truly thrilled to spouse with researchers like Eleftheria, whose team is producing new sustainable resources. And by partnering closely with researchers at Microsoft, we hope to acquire solutions that are scalable and deployable for field.
What kinds of new resources is the Roumeli group functioning on?
Eleftheria Roumeli: Our team focuses on building supplies derived from biological subject. In addition to seaweeds and other kinds of algae, this includes plant residues and microbial products. Our scientific tests intention to more our understanding of how these natural, multipurpose resources can be utilized as composite constructing blocks for sustainable choices to plastics.
How do you manufacture sustainable components—like biodegradable parts—for electronics?
ER: The wonderful factor is that today’s manufacturing solutions can be used to create sustainable components for electronics. For example, some of the biologically derived supplies my group functions with can be designed into inks and filaments for producing elements applying 3D printing. We recently revealed a paper describing inks we developed from spirulina cells—that’s a type of blue-inexperienced algae—both with and without cellulose fibers as a filler. Cellulose is the most abundant purely natural polymer, and these inks are 100% compostable in soil. You can find no specific composting facility essential!
What are other option filaments you can use for 3D printing?
ER: We can also make hybrid components that are a mix of both organic matter—such as spirulina cells—and industrial, degradable polymers. For the polymer, we use matrix elements these as polylactic acid, which Vikram stated just before and is the most commonly readily available industrially compostable polymer, or polybutylene adipate co-terephthalate, a soil-compostable polymer. The individual alternative of elements decides the houses, effectiveness and the compostability of our filaments.

For illustration, for packaging, which we typically obtain and “consume” incredibly rapidly and then discard instantly, a product made only of biological parts would be preferable. Then, soon after we use it, it could be disposed of in a backyard or landfill and it would degrade in a number of weeks.
But if we want a filament for the most popular form of 3D printer, we would require a polymer binder to make sure that the filament meets the demands of hot-extrusion dependent printing.
Are there any other new improvements for sustainable electronics?
Aniruddh Vashisth: A person issue we are working on is recyclable artificial polymers. As opposed to what Eleftheria’s team research, these polymers are not derived from biological components. In its place, these polymers consist of an adaptive community and can be recycled and reprocessed multiple moments.
In contrast to other plastics, these elements do not lose their thermo-mechanical houses through reprocessing and recycling. This is fascinating due to the fact you can reuse the exact product yet again and once again! This phenomenon of retaining material attributes is probable due to the fact the building blocks that make up these components can detach and reattach, just like Legos.
So when we are recycling, we are disassembling and reassembling the Legos. We have been concentrating on aerospace-quality composites, but we are setting up to check out other applications with a broad range of target apps.
What effect would that have on the e-squander trouble?
AV: Present-day e-squander is normally a advanced composite, with plastics, metallic and ceramic factors all in the exact same device. Recycling these elements is a demanding endeavor, so they usually just close up in landfills and guide to pollution.
Appropriate now there are additional than 250 million desktops and 7 billion phones in the globe. Most of these have polymer components. Just consider if the polymers utilised in these equipment could be recycled many situations. That would be a terrific step towards sustainability! Our group has been doing the job on how to design and characterize this sort of recycled polymer composites for a more sustainable foreseeable future.
Quotation:
Q&A: Creating Earth-friendly electronics (2022, April 21)
retrieved 27 April 2022
from https://techxplore.com/information/2022-04-qa-earth-friendly-electronics.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any reasonable dealing for the intent of private research or exploration, no
aspect could be reproduced with no the prepared permission. The content material is delivered for information reasons only.