Lots of of us depend on GPS (International Positioning Process) to estimate journey instances, uncover our way to new places, stay away from visitors congestion, continue to keep observe of the little ones, and commonly avoid receiving shed.
But it is not often the most trusted of programs, especially in developed-up parts the place it is really complicated to get a straight line of sight to and from a satellite.
Now scientists have occur up with a new and improved technologies that could ultimately switch GPS in some situations. Called SuperGPS, it’s exact inside of 10 centimeters (or 3.9 inches) and isn’t going to count on navigation satellite programs.
The new solution can make use of networks similar to cell networks, but as a substitute of streaming knowledge to our telephones the community gets a precise take care of on the device.
A mix of radio transmitters and fiber-optic networks sort the basis of the procedure, with some wise tweaks on prime.
“We recognized that with a couple chopping-edge improvements, the telecommunication community could be remodeled into a very exact option positioning system that is unbiased of GPS,” suggests physicist Jeroen Koelemeij from Vrije Universiteit Amsterdam in the Netherlands.
“We have succeeded and have efficiently developed a process that can give connectivity just like present cell and Wi-Fi networks do, as perfectly as exact positioning and time distribution like GPS.”
In a check website with six radio transmitters, the researchers had been ready to display their program in action throughout an location of 660 sq. meters (7,104 sq. ft). The timings of the transmitted radio alerts can be calculated and interpreted to gauge distance, which then reveals the placement of personal devices.
1 of the crucial parts of the new community positioing method is a synchronized atomic clock: perfect timing usually means more specific positioning. Essentially, the fiber optic cables act as connections that maintain every little thing in sync, and correct to a person billionth of a next.
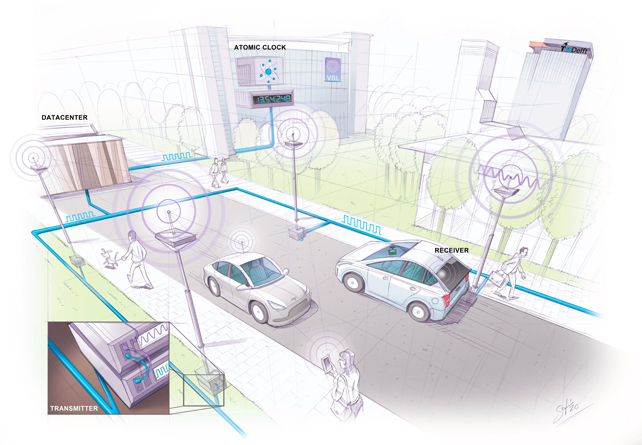
The process also deploys a radio sign bandwidth that is significantly bigger than normal – even though as radio spectrum bandwidth is high-priced owing to its scarcity, the team utilized quite a few smaller bandwidth radio indicators merged alongside one another to form a larger sized digital bandwidth for the network interaction.
This additional bandwidth overcomes just one of the largest complications with conventional GPS, which is that radio indicators get mirrored off structures and can immediately grow to be bewildered.
“This can make GPS unreliable in urban configurations, for occasion, which is a issue if we at any time want to use automatic vehicles,” states electrical engineer Christiaan Tiberius, from the Delft University of Technology in the Netherlands.
As nicely as automatic motor vehicles, the new process could be practical in setting up quantum communication networks and following-technology networks for cell products, according to the researchers who designed it.
Though